The three countries are hegemony, and the two are called emperors: Can BAT global attack Baidu counterattack with AI?
This article was first published on the WeChat public account: New Wisdom. The content of the article belongs to the author's personal opinion and does not represent the position of Hexun.com. Investors should act accordingly, at their own risk. [Introduction to Xinzhiyuan] On April 20th, The Economist published an article entitled "Three Kingdoms Hegemony, Two Emperors: China's Internet Giants Going Global", specifically analyzing BAT's three Internet giants in international and domestic The current development trend, analogy to Yahoo, draws the conclusion that "Baidu is already behind." The article also mentioned that Baidu will put the future bet on the AI. New Wisdom brings the introduction of BAT's latest actions on AI, outlines the latest competitive landscape, can Baidu rise again with AI? In addition, as the Economist article finally reminds, whether in AI or other areas, the profitable domestic battlefield behind the international BAT is truly not to be ignored. Not long ago, Silicon Valley investors dismissed large Chinese Internet companies and thought they were copying Western products. But now things have changed, because these companies have become a behemoth of growing international ambitions. The article introduces the development of the current three companies at the beginning. The article mentioned that Alibaba is China's largest e-commerce group, processing more transactions per year than eBay and Amazon combined. Alibaba Chairman Ma Yun promised to serve 2 billion consumers worldwide within 20 years. Tencent, specializing in online games and social media, is now the 10th largest listed company in the global market capitalization with a market capitalization of approximately $275 billion. Ma Huateng, chairman of Tencent, hopes that China will “lead the future global science and technology revolutionâ€. Unlike the introduction of Alibaba and Tencent, when the author mentions Baidu, the author describes: "With Ali and Tencent are gradually growing into the international backbone. Baidu is the third member of China's three major Internet giants "BAT" behind." Baidu is becoming Yahoo in China? The Economist article further analyzes the current status of the three BAT companies, emphasizing that the international competition among the three companies is increasing. The author further writes that the huge domestic market did not stop the bloody war of BAT competing for the sphere of influence. But the results of this war quickly became clear: Tencent and Alibaba are all making rapid progress; while Baidu has many of its own goals, it is far behind the former two. For Baidu, the common view of domestic experts is that it is becoming Yahoo in China. Yahoo was once the dominant search giant, declining due to lack of innovation and a series of management mistakes. The article gives an analysis of the income of the three companies: Baidu's revenue revenue growth rate in 2016 fell to 6.3%, much lower than the 35% in 2015 and 54% in 2014. About 90% of the company's revenue comes from online advertising, but as advertisers shift spending on Baidu search ads to social networking sites such as WeChat and Alibaba's mobile e-commerce platform, Baidu's revenue has plummeted. Jingdong Mall adopts an “asset-heavy†business model similar to Amazon USA. So far, JD's huge investment in warehouses, logistics and express delivery is not as good as Alibaba, but last year the company's revenue reached 37.5 billion US dollars, higher than the previous year's 28 billion US dollars. Its business-to-consumer market share in China rose to 25% in 2016, up from 18% at the end of 2014. If JD's investment in infrastructure begins to pay off, Alibaba's future domestic growth may be at risk. In analyzing the income of the three companies, the author mentioned that although Baidu has lagged behind the other two giants in revenue, Baidu continues to expand, trying to keep its artificial intelligence, online video, virtual reality and augmented reality technology, and Online to offline, (O2O) services and other aspects of the bet. But some people are pessimistic about their future: "There are almost no opportunities in these areas in five years." BAT's sea strategy: acquisition and talent The Economist article argues that BAT's strategy abroad can be summarized as acquisitions and talent. Tencent is also boldly acquiring overseas. It spent $8.6 billion last year to acquire Finnish Supercell, a deal that has made Tencent the world's largest online game provider. Together with Taiwan's Foxconn (a contract manufacturing giant), Tencent invested $175 million last year in the Indian messaging app Hike Messenger (similar to WhatsApp in the US). Tencent is also an early investor in Snapchat in the US, and Snapchat is another popular messaging app, with its parent company Snap coming out in March. One reason for these acquisitions was that Tencent’s efforts to promote WeChat overseas earlier were unsuccessful (including a wave of publicity campaigns in Europe and Messi’s appearance). Social networks like Facebook and WhatsApp have been built and proven to be untouchable. At the same time they are copying other people's successful experiences: Once they adopt the innovations on WeChat, what reasons does Western consumers have to turn to social networks from China? These investments have been targeted at Tencent’s core business, away from the sites already occupied by Alibaba and Baidu. Sometimes the three eventually come together – if not originally designed. For example, they are behind the scenes of Didi Chuan (a car rental company that looks globally), but in other respects, the domestic wars of BAT are spreading to foreign markets. The Economist said that Baidu's overseas promotion is mainly to acquire talents in the fields of machine learning and AI. The company has begun its first recruitment at top universities in the United States, including Stanford University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Although AI leader Wu Enda has recently left, Baidu still has an AI lab that is indispensable in Silicon Valley. Lin Yuanqing, Dean of Baidu Research Institute, is responsible for deep learning, big data labs, Silicon Valley artificial intelligence labs, and the augmented reality labs added last year. At the media meeting on April 5 this year, regarding the departure of Wu Enda, Lin Yuanqing said: "In the whole process, I personally did not feel some very big changes. The only change is that he left, others are still quite Stable, that is, the entire team, the coordination of the entire resources should be the same." However, Baidu has different firepower from Alibaba and Tencent. It tried to conquer Japan and other overseas markets through its search engine and failed to do so. It also recently opened autopilot technology to its competitors. The Economist believes that, as Tesla did in 2014, Baidu still has a long way to go to make a huge impact on the unmanned vehicle sector. Baidu who will bet on machine learning and AI in the future According to a report released by research firm EMarketer in September last year, in the Internet advertising market, Alibaba has surpassed Baidu to become the market leader. Earlier, Bloomberg wrote in a report on Baidu's entry into artificial intelligence that Baidu, which had been established for 17 years, had tried to develop a diversified Internet economy, but the results were mixed and unspeakable. In the first 12 months of February 2017, Baidu’s group-buying website 糯米’s daily page views decreased by 59%; Wu Yue, an analyst at China International Financial Center, analyzed that Baidu’s take-away sales had fallen to third place. According to analyst Ella Ji of Huaxing Capital (Hong Kong) Co., Ltd., Baidu's streaming video service website, iQiyi, is extremely popular, but it still needs to spend 12 billion yuan to maintain its content. Bloomberg said in the report that these precarious data points to Baidu's move to enter AI. Tencent also recently invested $1.8 billion in Tesla in the United States. This is especially a challenge for Baidu, because Baidu is betting on machine learning and AI in the future. Baidu is the earliest company to develop on artificial intelligence. In late 2013, the Institute of Deep Learning was established. In 2014, it was renamed Baidu Deep Learning Lab (IDL). Wu Enda was the head of the department. In Beijing, Shenzhen, Shanghai and Silicon Valley, there are 1,300 people. To expand the recruit. In February of this year, the National Development and Reform Commission officially approved the establishment of the National AI Laboratory by Baidu, which was also regarded as the final landing of the "Chinese brain" of the Li Yanhong proposal. At the unveiling ceremony, Li Yanhong said that in the past two and a half years, Baidu has invested RMB 20 billion in various R&D projects, most of which are in the AI ​​field. With the speech recognition framework DeepSpeech, the open source deep learning platform PaddlePaddle and Baidu smart car project as representatives, Baidu's accumulation in the AI ​​field is obvious to all. However, a series of high-level personnel changes have recently made this giant avatar in the AI ​​storm, turbulent. In June 2015, Yu Kai, deputy dean of Baidu Research Institute and director of Baidu Deep Learning Lab, resigned. In the same period, IDL outstanding scientist Wu Ren was resigned. In December 2015, Ni Kai, head of Baidu's driverless car team, left. In December 2016, Baidu unmanned vehicle architect James Peng and Lou Tiancheng resigned. In March 2017, Wang Jin, senior vice president of Baidu and former general manager of the autonomous driving division, resigned. Of course, the most sensational is April 2017, Baidu AI core figure, Baidu chief scientist Wu Enda officially resigned. Wu Enda said in his letter of departure that Baidu is one of the few companies with world-class expert expertise in all important areas of AI, including voice, natural language processing, computer vision, machine learning, and knowledge mapping. Now, these foundations were taken over by Lu Qi, former Microsoft executive vice president of Microsoft, who joined Baidu in January this year. According to the previous report of Xinzhiyuan, Lu Qi joined Baidu as the president and chief operating officer of Baidu Group, the director of Baidu and the vice chairman of the board of directors. He is mainly responsible for Baidu's products, technology, sales and marketing operations, and also serves as Baidu's smart driving business group. General manager. After Lu Qi took office, he quickly carried out a drastic restructuring and reform: in February, the original secret team was upgraded to the secret division, accelerating Baidu's artificial intelligence strategic layout and artificial intelligence productization and marketization; on the same day, Baidu also announced a wholly-owned acquisition of Raven Tech. After 90, the founder of the company, Lu Wei, joined the team with Baidu and served as general manager of smart home hardware, reporting directly to Lu Qi. In March, the Intelligent Driving Group (IDG) was established to integrate the original Automated Driving Division (L4), Smart Vehicle Division (L3) and Car Life etc., with Lu Qi as General Manager. On April 13, Baidu acquired Silicon Valley AI computer vision startup xPerception. On the past April 19th, Lu Qi announced the “Apollo†program at the Shanghai Auto Show, which fully opened Baidu's autopilot technology to the industry, including vehicle platforms, hardware platforms, software platforms and cloud data services. Baidu will open code or capabilities for environmental awareness, path planning, vehicle control, in-vehicle operating systems and more, and provide complete development testing tools. For the Apollo program, Lu Qi said that there are "three goals: First, the core platform: We hope to establish a unified technology platform; Second, shared services: shared services and high-tech; Third, the solution: build a holistic solution ". Alibaba and Tencent, who are secretly working on AI In April 2017, Tencent Artificial Intelligence Lab (AI Lab) announced that Zhang Wei, the top scientist in the field of artificial intelligence, will be the first person in charge of Tencent Artificial Intelligence Laboratory. Zhang Wei was previously a researcher at IBM Research Institute, a research fellow at Yahoo Research Institute, a vice president of Baidu Research Institute, and a head of the Big Data Lab. Soon after, Tencent AI Lab official website once again released news, Yu Dong, who worked for Microsoft Corporation for 19 years and served as the chief researcher of Microsoft Research Institute, joined Tencent as an outstanding scientist and deputy general manager of the artificial intelligence laboratory. Yu Dong is a senior expert in speech recognition and deep learning. At the same time, Liu Wei, a former research scientist at the IBM Watson Research Center, also served as director of the AI ​​Lab Computer Vision Center, responsible for AI research related to image and video data. On March 27th, at the Xinzhiyuan 2017 Open Source·Eco AI Technology Summit, Zhang Wei made his debut speech. He first introduced the direction of AI Lab: AI Lab valued the underlying and basic technology research, such as algorithmic ability is to rely on machine learning. . On the machine learning, look at how the machine looks, that is, computer vision; how the machine listens, that is, speech recognition; how the machine understands, is natural language processing, including text and interaction. After completing these basic researches, and then applying them to the business level, you can directly generate value for the company. Dr. Zhang Wei will be the first person in charge of Tencent AI Lab, leading more than 50 AI scientists and more than 200 AI application engineers to focus on basic research in artificial intelligence, including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing and machines. Learn these four vertical areas. At the same time, based on Tencent's own business needs, Tencent AI Lab will also cooperate in research and application in the four directions of content, social, gaming and platform tool AI. On April 2, Shenzhen IT Leaders Summit, Tencent CEO Ma Huateng said that Tencent has recruited a lot of AI talents in a year and has set up a laboratory in Seattle. On the other hand, Alibaba is constantly adjusting its AI strategy. On March 9th, at the first technical conference of Alibaba, CEO Ma Yun announced the launch of a program codenamed "NASA", which will build a strong independent R&D department for the next 20 years, involving machine learning, chips, IoT, operating systems, and biology. Identify and other core technologies. Ma Yun said: "The artificial intelligence is very hot recently, so it is better to do the machine intelligence." Ma Yun’s “NASA†program is considered to be an important signal for the strategic layout of Ali Artificial Intelligence. According to industry rumors, Ali's Institute of Data Science and Technology (IDST) will be reorganized into a new artificial intelligence research institute. Obviously, in the competition of artificial intelligence, Alibaba is also well prepared. In the first Yunqi Conference in 2017, Alibaba Cloud President Hu Xiaoming delivered a speech on “The Road to Intelligenceâ€. In an exclusive interview with Xinzhiyuan, Hu Xiaoming said: "In addition to cloud computing big data, more emphasis is placed on the deep impact of artificial intelligence and machine intelligence on the industry. The Internet allows all data to be online, while data is online, we can make data a resource. , participate in decision making." Recently, Alibaba Cognitive Computing Lab, in collaboration with the University of London School of Computer Science, has released a new study that examines the micro-combat scenarios in the game "StarCraft" as a test environment, intensively studying between multiple AI agents. Collaborative issues are designed to solve problems that humans are not good at through collaborative intelligence. This is Alibaba's latest development in general artificial intelligence research, showing the company's strong determination in researching AI's cutting-edge technology. It is definitely wrong to ignore the domestically profitable market. As the Economist article says, BAT is not only hot in the country, but also actively deployed in the globalization strategy. Baidu, who is in a backward position, has placed a bet on the AI, and has achieved a certain level of technology and talent accumulation with its first-mover advantage. At the same time, whether it is Alibaba or Tencent, the power of AI can not be underestimated. In the strategy of globalization, AI has become an indispensable part of it, whether it is market, talent or technology. In addition, the crucial point is. Although the foreign media still holds a suspicious attitude towards BAT's globalization strategy, one thing is worthy of recognition: it is definitely wrong to ignore the domestically profitable market. This is true whether it is in AI or otherwise. Baseball Hat Cap,Baseball Cap Safety Hat,Cotton Baseball Caps,Breathable And Comfortable Sport Cap Jingjiang Pingdong Import&Export Co.,Ltd , https://www.socksjjpd.com![[Depth] Three countries for hegemony, two emperors: BAT global attack, Baidu can rely on AI counterattack?](http://i.bosscdn.com/blog/d4/1d/76/f58d686356a16ac6fd7e7c4831.jpg)
Yuan-chi of the new report: Wen Qiang Zhang Yi Liu Xiaoqin Ferguson
On April 20th, the Economist published an article entitled "Three kingdoms, two empires: China's internet giants go global" on the current issue. BAT conducted an in-depth analysis of the competitive situation at home and abroad. 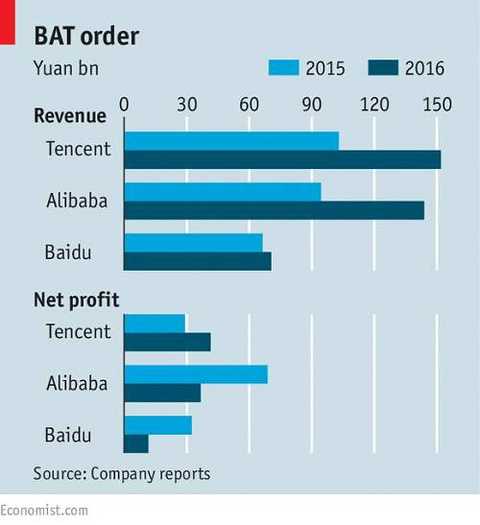
Tencent is probably the most terrible of the other two giant companies. Tencent's revenue and profits are higher than Alibaba (see table above). As it began to place ads on WeChat (as long as it hasn't caused a lot of objection from users), its market value will rise again. In fact, Tencent’s main weapon against Alibaba is its holding of Jingdong, the second largest e-commerce platform in China. Founder Liu Qiangdong is one of the most ambitious and successful consecutive entrepreneurs in China. 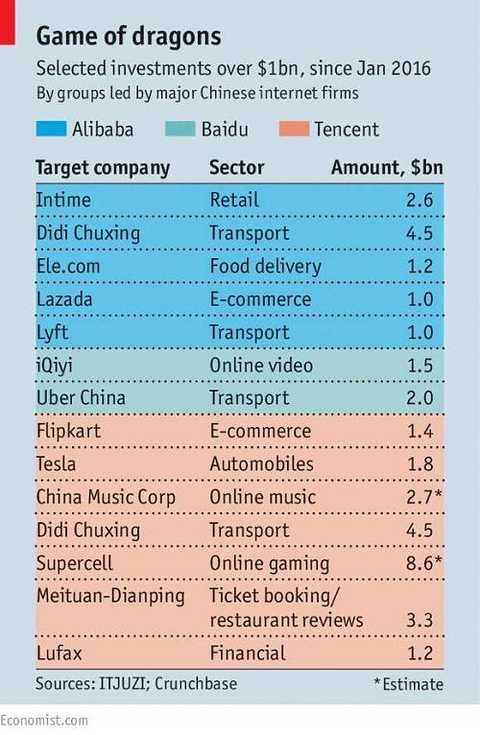
Specifically, the main weapon of Alibaba's globalization is Ant Financial. Ant Financial has invested in local online payment companies in Thailand, the Philippines, Singapore and South Korea. In the United States, Ant King bought the MoneyGram International.